Diet for dogs with kidney disease
Updated February 2024, by Kristina Johansen
In this guide to diet for dogs with kidney disease, our primary focus will be on food. However, we will also delve into various relevant topics, such as:
- Chronic versus acute kidney disease.
- The function and role of your dog’s kidneys.
- Recognising the signs and symptoms of kidney failure in dogs.
- Why hydration is essential for kidney health.
Let’s begin with a bit of basics.
Chronic versus acute kidney disease
There are two types of canine kidney disease – chronic and acute.
Acute kidney disease usually presents very suddenly and reverses more easily than chronic forms of the disease.
On the other hand, chronic kidney disease (CKD) is more long-term and doesn’t always present suddenly but instead can develop over time.
The treatment and prognosis for dogs diagnosed with CKD differs from that for dogs with an acute form of the disease. In this blog, I will focus on chronic kidney disease in dogs, not acute kidney disease.
What do my dog’s kidneys do?
The kidneys’ main role is to filter waste products from the blood via urine. Old cells, the digestive process (food), medications, and even poisons generate the waste products that the kidneys remove.
Over 1 million tiny tubes (per kidney) called nephrons perform the filtering. As blood passes from the capillaries through the nephrons, essential chemicals and molecules are kept, while waste products are removed and passed into urine collecting tubes. They are then expelled from your dog’s body with water as urine.
But filtering blood isn’t all these small but complex organs do. Your dog’s kidneys also help regulate
- The amount of water in the blood;
- Urine production;
- Potassium and sodium levels.
On top of all this, the kidneys produce three important hormones:
- Calcitriol – a form of vitamin D which helps calcium absorption and so keeps bones healthy
- Erythropoietin – tells the bone marrow to produce red blood cells
- Renin – helps regulate blood pressure
Given their wide range of essential functions, it’s unsurprising that if the kidneys become damaged or compromised, it can lead to serious health issues.
What are the signs and symptoms of kidney failure in dogs?
There are a number of signs and symptoms of CKD that you can keep an eye out for in your dog.
These include:
- Increase water consumption and increased urine output
- Vomiting
- Diarrhoea
- Decreased or lack of urine output
- Blood in the urine
- Lack of appetite and weight loss
Unfortunately, most of these signs are not specific to chronic kidney disease (CKD). Considering the wide range of functions performed by the kidneys, the symptoms of CKD can and do vary between dogs.
That’s why it’s important to be aware of what’s normal for your dog. If you notice anything unusual about their behaviour or habits, speak to your vet immediately.
When physically examining your dog, your vet may find other signs or indicators of kidney failure, including:
- Pale gums as a result of anaemia
- Ulcers on the tongue, inside cheek or gums
- Enlarged abdomen or swollen limbs due to fluid build-up
Diet for dogs with chronic kidney disease
It can be very worrying to hear that your dog is diagnosed with kidney disease. However, please take some comfort in knowing that a carefully considered diet is key and can significantly improve your dog’s quality of life and longevity.
To illustrate just how crucial dietary intervention is, take a look at these numbers from one of my clients before and six weeks after implementing a dietary change:
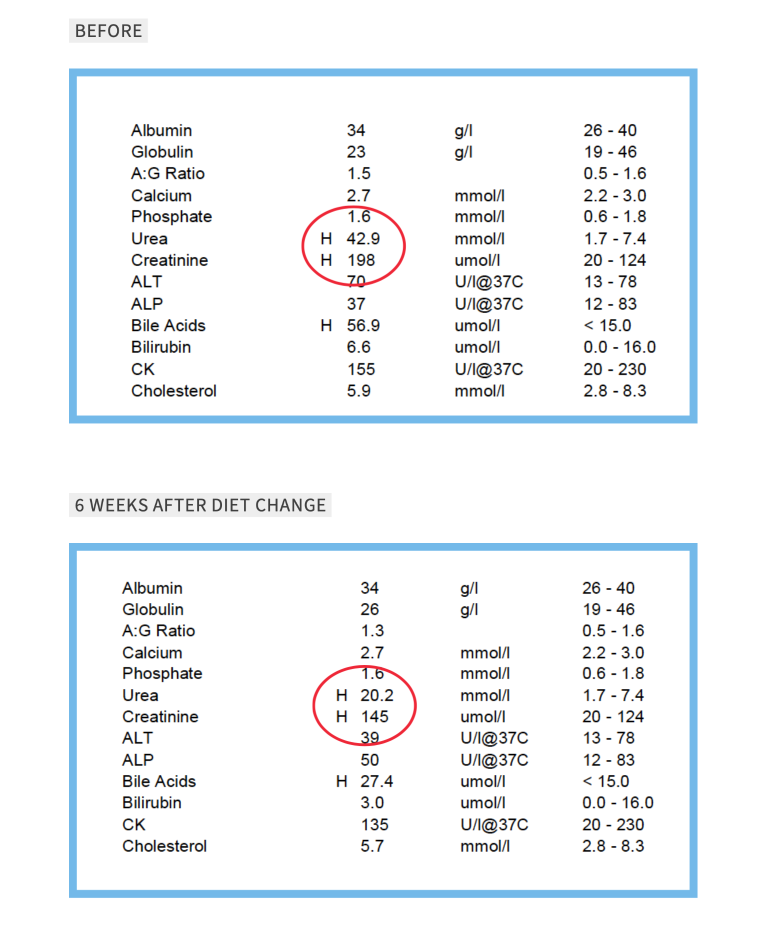
So, what diet changes should you be making?
Protein
Despite ongoing debate, it’s still widely recommended that dogs with kidney disease should be fed a protein restricted diet. There are two main reasons for this:
- Your dog’s kidneys filter waste (urea) from protein metabolism. The more protein waste there is to remove, the harder the kidneys need to work. This can put additional stress on the already struggling kidneys, causing them to deteriorate faster.
- If the kidneys can’t remove all the extra waste, it can build up in your dog’s blood. Excess urea can lead to symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, lethargy, and loss of appetite.
Therefore, by limiting the amount of protein in the diet, we can alleviate this strain and reduce these symptoms.
Of course, ‘restricted’ is a relative term, and there is no clear consensus on the precise level to which protein intake should be reduced for dogs with kidney failure. The need for restriction varies from one dog to another, depending on individual health and the progression of the disease. The best indication of a need to reduce protein is when concentrations of urea and other nitrogenous substances show up on test results.
It’s not just about lowering protein intake; the type of protein you feed is also important. That’s why it’s essential to consider something called the Biological Value (BV) when choosing the best protein for dogs with kidney disease.
BV measures how efficiently your dog’s body uses protein. Proteins with higher biological values are absorbed and utilised more effectively, producing less waste, which is especially important for dogs with kidney disease.
Good sources of high-quality protein include:
- Eggs
- Meat
- Dairy Products
- Fish
- Poultry
Phosphorus
Dogs with kidney failure struggle to excrete excess phosphorous in their urine, which can lead to further kidney damage. So, while an important component of a healthy dog’s diet, phosphorous should be restricted in dogs with kidney disease.
Again, ‘restricted’ is a relative term. Your dog’s phosphorus needs depend on their kidney function. Ideally, phosphorus should be reduced in line with creatinine and blood phosphorus readings.
Foods highest in phosphorus include raw bones, dairy products, organ meats, and egg yolks. That does not mean not feeding these foods at all; the goal is to restrict phosphorus, not remove it.
Sodium (aka salt)
When it comes to sodium, there are clear benefits to restricting it in the diets of people with CKD (it’s been shown to decrease arterial hypertension.) However, there isn’t the same evidence to show that reducing sodium below NRC recommendations benefits dogs with kidney failure. The role sodium plays in kidney disease in dogs is not fully understood. By and large, it’s recommended that sodium levels should only be restricted moderately. This is because while excessive sodium levels can be detrimental, so can extreme restriction of the compound.
Vitamin B-compounds
Another consequence of excessive urination due to kidney failure is the loss of vitamins, particularly B vitamins (e.g., thiamine, folic acid, and cobalamin). Therefore, including vitamin B supplements and foods high in vitamin B (for example, meat, fish and eggs) in the diet of dogs with CKD is important to avoid deficiency.
Fatty acids
Certain types of fat – namely omega-3 fatty acids – can slow the decline of kidney function associated with CKD. For this reason, I always include omega-3 fatty acids in the diet of dogs with kidney failure. In particular, look for EPA and DHA (the good stuff). EPA and DHA can be added by using supplements such as fish body oil (not cod liver oil) or by including foods rich in them, such as mackerel or sardines, in your dog’s diet. You can learn more about fish oil and how to choose the best one for your dog by heading to this blog:
How to choose the best fish oil for your dog
Antioxidants
Chronic kidney disease is most commonly found in older dogs, and it’s believed that oxidative damage, caused by free radicals, contributes to its progression. This is where antioxidants come into play, as they have a crucial role in controlling the harm caused by these free radicals.
We’ve all heard about antioxidants, but what exactly are they?
Imagine your dog’s body as a beautiful garden and free radicals as weeds. Without proper control, these weeds will overrun the garden. Antioxidants are like gardeners who keep the weeds in check, ensuring the garden remains healthy and everything grows well.
In dogs with kidney disease, more weeds (free radicals) are growing, but there are fewer gardeners (antioxidants) to control them. This imbalance can stress the garden and lead to problems.
Adding antioxidants to your dog’s diet is like adding more gardeners to manage the weeds.
To boost your dog’s dietary intake of antioxidants, simply add fruits and vegetables to their diet. You can find tips and advice on how to best do this in this blog.
Boosting Your Dog’s Health: Choosing and Including Fruits and Vegetables
Why hydration is important for kidney health
One of the key roles of your dog’s kidneys is to filter out waste through urine. In cases of chronic kidney disease, the kidneys lose their ability to concentrate urine, which means they need more water to flush out waste. Consequently, dogs with CKD often drink and urinate more. Ensuring your dog has enough water is crucial to keeping them well hydrated and supporting their kidney health.
Water needs can be met by a combination of water consumed via drinking and water as a component of food. Generally, dry dog food contains 8 to 10% water. In comparison, canned food is about 75% water. The water content of fresh foods is highly variable. For example, a cucumber is approximately 96% water, and a boiled egg is 75% water. Therefore, canned or fresh foods are preferred for dogs with kidney failure.
If your dog is reluctant to drink enough water, adding a dash of flavour to the water bowl can help. Here are a few ideas:
- Meat or vegetable broth
- Canned tuna or salmon water
- Watermelon Juice
- Coconut Water
Key takeaways for managing CKD
Managing chronic kidney disease in dogs may initially seem overwhelming. However, with a thorough understanding of your dog’s dietary needs, you can significantly enhance their quality of life and longevity.
Key nutritional goals include:
- Opt for a high-moisture diet.
- Enhance the diet by incorporating EPA and DHA, along with antioxidant-rich foods.
- Restrict phosphorus and protein intake
- Choose proteins with high biological value
- Ensure adequate water intake for proper hydration.
We have reached the end of the blog, and I hope the information has given you a better understanding of managing your dog’s kidney disease successfully. If you have any questions or need further help, don’t hesitate to get in touch. You can reach me at kristina@elmoskitchen.com. Your feedback and suggestions are always welcome.
Meet Pickles
Before you go, I would like to introduce you to Pickles and share this lovely message I received from her owner.
“Pickles was diagnosed with CKD two years ago and recently the disease has started progressing. With a change of diet, within two weeks, I have a dog who is eating again, has no tummy pain, is sleeping through the night and is as regular as clockwork!!! She is also loving life again; chasing squirrels like there is no tomorrow, not bad for an old lady of 13 years, let alone one with CKD!
The transformation in just two weeks is unbelievable. Thank you again Kristina and I sincerely look forward to working with you to give my beloved Pickles the best quality of life, for as long as she has on earth.”

If you would like a deeper understanding of Chronic Kidney Disease in dogs and its nutritional management, I have written a comprehensive book on the subject. The book expands on the information in this blog, providing a deeper knowledge, practical advice, treat recipes and additional resources. You can find the book here:
Diet & Health Advice
If you have a dog with CKD and would like to book a consultation, please email us; we’ll be happy to help.
Book a Consultation
